Challenges Facing Global Buyers of Hot Isostatic Pressing Equipment
The global market for Hot Isostatic Pressing Equipment has seen substantial growth in recent years, significantly driven by demand for advanced manufacturing technologies in various industries. According to the report produced by MarketsandMarkets, the hot isostatic pressing market is projected to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2021. Key among these is the need for materials with mechanical properties for applications that serve the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. A number of obstacles are faced by international buyers in acquiring such complex machinery even while the market seems ready for a spurt.
Among them, one of the primary challenges remains the speed of technology development in the industry, thereby compelling manufacturers to rise to changes in production methods and equipment. Moreover, the procurement of Hot Isostatic Pressing Equipment is hindered by supply chain issues such as shortage of key raw materials and shipping delays further aggravated by geopolitical tensions. A Deloitte survey found that 63% of manufacturing executives are concerned that supply chain disruptions could cause operational inefficiencies. Global buyers need to know about such challenges in order to formulate decisions about Hot Isostatic Pressing Equipment and to plan their investments in equipment best suited to meeting their specific production requirements.
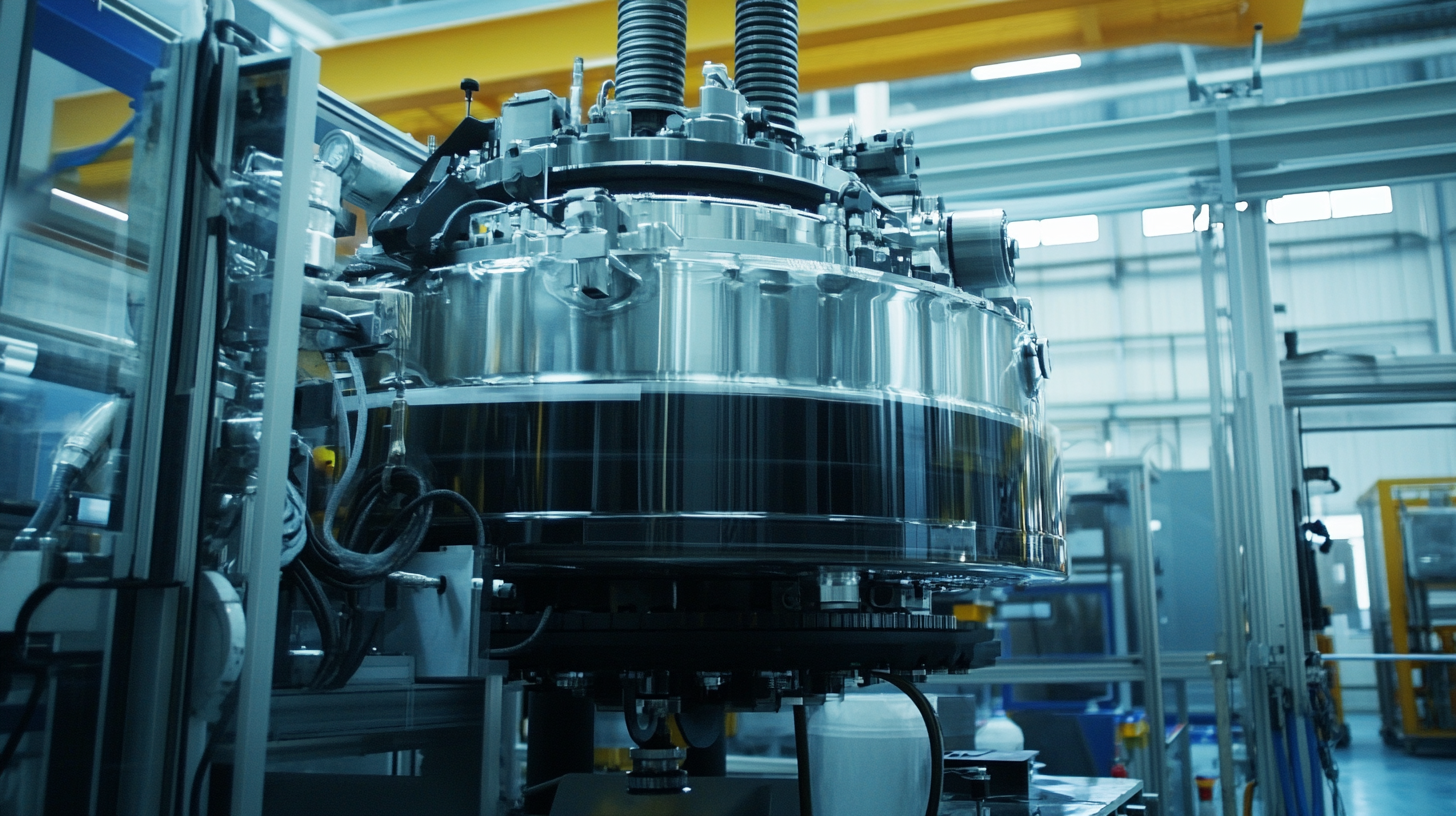
Understanding the Hot Isostatic Pressing Equipment Market Dynamics
The hot isostatic pressing (HIP) equipment market is in a stage of necessary evolution. There have been several recent developments including the introduction of new models with enhanced capabilities that increase the functionality of HIP systems. For example, the newest press models allow different processes to be performed at the same site. This does streamline operations and improves their efficiency as well as reduces manufacturer operating costs. In addition to this, high-performance material demands increase in the industries, particularly aerospace, which propels the applications of HIP technologies. The recent installations of large HIP systems within companies targeting aerospace components denote that the technology is vital for producing components capable of meeting tight performance specifications. As manufacturers work towards flexibility and increased output capacity, the advancement of property improvement by HIP will be an analytical factor in the decision-making process regarding equipment purchase. Research findings are also changing the market dynamics regarding many effects emanating from HIP such as corrosion resistance of titanium alloys. These give the specific buyer information about both the working conditions to be expected from the HIP unit and possible improvements in the product quality and durability of a finished product. The general understanding of this changing environment is essential for buyers from the world to make better choices within an increasingly competitive landscape.

Key Challenges in Sourcing Hot Isostatic Pressing Technologies Globally
Sourcing advanced technologies such as Hot Isostatic Pressing(HIP) equipment presents a major challenge for the global market buyer. One of the challenges is dealing with the myriad manufacturers and suppliers who comprise the serpentine landscape. Each company under consideration may present differing levels of quality and technological advancement with varying degrees of service support. It becomes almost compulsory for buyers to observe due diligence at all possible levels. Understanding the differences between competing technologies and their respective uses might be even daunting for companies preparing to implement HIP processes effectively.
Apart from that, global buyers also encounter logistical constraints such as shipping and installation cost which vary from one vendor to another depending on the origin of the equipment and delivery destination. Supply chain disruptions due to political tensions or pandemics disrupt the acquisition further. That kind of uncertainness calls for coordination and collaboration with supply partners to ensure the buyer has an expected timely installation and delivery post-delivery support. The buyer also has to consider the availability of spare parts and maintenance services in the locale because this has a direct significance on the life and productivity of the system.
The regulations bypass another fascinating layer of complexity. A country has its standards and certifications for manufacturing technologies. Buyers have to ensure that the HIP equipment overcomes the local regulations besides being compliant with industry-specific requirements. This usually demands more investment on training and resource allocation to cover all compliance measures, which emphasizes the need for a collective approach regarding HIP equipment procurement within the international arena.
Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Issues in Different Regions
Global purchasers have acquired new dimensions concerning compliance and regulatory issues when procuring Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) equipment. These diversifications tacitly transgress that which particular regions view as standards and regulate them under different parameters that create a blanket of complexity for companies investing in this technology. However, this creates room for the creation of standards that differ across the region, making one generalizing approach impossible. It is important for buyers to be thorough in understanding specific local laws that control manufacturing processes, safety protocols, and the environmental effects of such equipment regarding the installation of HIP equipment.
In the European Union, for example, strict CE marking requirement adherence is mandatory, entailing that the equipment conforms to set safety and health standards. On the contrary, in the United States, buyers need to comply with certain OSHA regulations as well as those from different industry standards, some of which may have varying implications concerning worker safety and equipment performance. Such differences may cause complications, especially for multinational companies engaged to work within many jurisdictions. It is very important for buyers to consider confirming with local experts on compliance so that they streamline the entire purchasing process while avoiding legal pitfalls.
Moreover, compliance with increasing emotive environmental regulations, which would affect the framework and progress within which HIP equipment would be designed and manufactured, is expected of companies. An offer from these companies includes proof compliance with emissions standards and promotion of sustainability initiatives. The latter show the global trend towards this manufacturing practice aligning itself with environmental concerns. Suppliers that pass such tests should not only match the regulations but also some corporate social responsibility goals with which their customers agree. Once these compliance challenges are studied and navigated, global buyers become empowered to make choices that strengthen their supply chains and enhance operational efficiency.

Evaluating Supplier Capabilities and Reliability for Quality Assurance
In the fast-changing world of manufacturing, especially in industries dependent on hot isostatic pressing (HIP) equipment, supplier-capability and reliability assessments have become an integral part of quality assurance. In a rapidly globalizing sourcing environment for manufacturers, the consideration of factors concerning supplier assessments cannot ever be put enough emphasis. MarketsandMarkets recently reported that the global HIP equipment market is anticipated to hit $2.4 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 5.1%. With this growth, other advanced manufacturing technologies are fast gaining favor, and the importance of supplier selection is gaining gravitas.
One important aspect of supplier evaluations is the focus on technology know-how and innovation capability. Companies should analyze factors such as production processes, quality control systems, and certification serials like ISO 9001 or AS9100, which represent adherence to exacting quality management requirements. Furthermore, Deloitte's survey found that 56 percent of enterprises suffering supply chain disruptions in 2022 acknowledged lack of supplier reliability as one of the major challenges. This statistic indicates there is a need for a rigorous vetting process that will ensure that suppliers are reliable in consistently meeting production and delivery timelines.
Furthermore, financial stability and customer support services weigh highly when it comes to prospective suppliers in the HIP equipment industry. A company's ability to provide ongoing technical support and after-sales service can decisively influence equipment performance and service life. McKinsey reported that successful collaborations among suppliers could enhance supply chain resilience by as much as 75% and thereby minimize supplier-related risks considerably. As global buyers face these challenges, a strategic approach to evaluating supplier reliability will offer firms a competitive advantage in the ever-changing manufacturing environment.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions on Hot Isostatic Pressing Investments
The hot isostatic pressing (HIP) landscape across the globe is now being influenced brutally by supply chain disruptions. For global buyers, increased deliberation in decision-making is occurring every day over issues such as delayed shipments, volatile materials costs, and unpredictable availability of components. All these lead to longer lead times for equipment procurement, with very critical manufacturing processes stalled and overall productive capacity affected.
Facing massive disruptions, many organizations are reshaping their supply chains to enhance resilience. Some are looking to diversify their sources, while some are ramping up investments in local manufacturing for risk mitigation from overseas dependence. Again, they are cultivating the supplier relationships while demanding more transparency in times of uncertainties. This fosters not only timely deliveries but also more flexible production .
Moreover, it encourages thorough assessment under the current circumstances for existing HIP investments. Buyers are compelled to negotiate urgency against the fallout of related financial costs due to supply chain instability. So, most buyers thus tend to develop a phased investment scheme that upgrades in increments while keeping operational flexibility. Thus, immediate needs are fulfilled while preparing companies for emerging market fluctuations, which translates into a more sustainable business model over time.