What is Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work?
Die Casting Molds play a crucial role in manufacturing. They are essential for producing metal parts efficiently. "The precision of die casting molds can significantly impact product quality," says John Smith, a die casting industry expert. This statement highlights their importance.
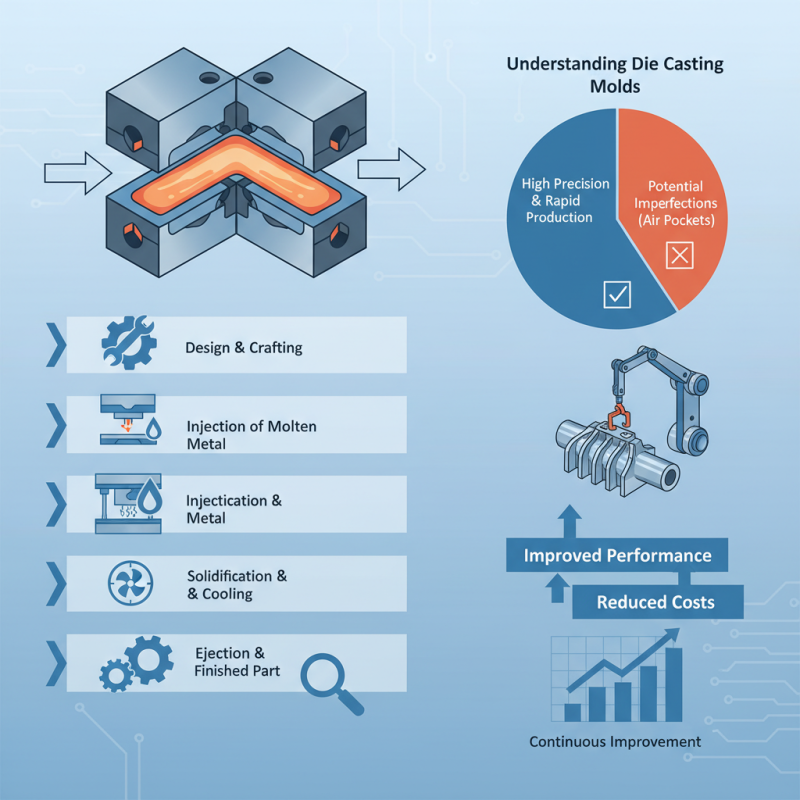
These molds are specifically designed to shape molten metal into desired forms. They allow for rapid production and create complex geometries. However, there can be issues with imperfections, such as air pockets or surface blemishes. Each mold must be carefully crafted and maintained to minimize these defects.
Understanding die casting molds is vital for manufacturers. It can lead to improved performance and reduced costs. Mistakes in design or execution may lead to wasted material or subpar products. Reflecting on these challenges is essential for continuous improvement in the industry.
Understanding the Basics of Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds are essential tools in the manufacturing process. They create precise shapes for various components. Made from durable materials, these molds can withstand high temperatures and pressure. The process involves injecting molten metal into the mold cavity. Once cooled, the mold opens to reveal the cast part.
Understanding die casting molds starts with their design. They often come in two pieces: the mold body and the core. The design needs to allow for easy ejection of the part without damaging it. This requires careful consideration of dimensions and angles. Flaws can occur if the design is not well thought out.
The cooling phase is critical. Uneven cooling can lead to defects like warping or cracking. It is vital to monitor the temperature closely. Additionally, regular maintenance of molds is necessary. Wear and tear can affect production quality. This aspect often goes unnoticed until problems arise in the output.
What is Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work?
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium |
| Mold Type | Single Cavity, Multi Cavity |
| Mold Life | 10,000 - 100,000 cycles |
| Cooling Time | 2 - 20 seconds |
| Injection Pressure | 1500 - 20000 psi |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, Electronics, Industrial Equipment |
| Benefits | High precision, Fast production, Excellent surface finish |
Types of Die Casting Molds and Their Applications
Die casting molds are essential in the manufacturing of various metal products. They allow for high-volume production with excellent precision. There are several types of die casting molds, each designed for specific applications.
One common type is the single cavity mold. It produces one part per cycle, making it ideal for high-quality, small-scale production. On the other hand, multi-cavity molds create multiple parts simultaneously, which boosts efficiency. However, they can be complex and may require more maintenance.
Additionally, there are inserts and core molds. Inserts allow for the creation of complex shapes, while core molds are used to form internal cavities. These molds ensure that intricate designs can be achieved, but they can also complicate the manufacturing process. Each type has its strengths and limitations, prompting manufacturers to choose wisely based on their needs.
Types of Die Casting Molds and Their Applications
This chart illustrates the distribution of applications for different types of die casting molds. Aluminum molds are predominantly used, followed by zinc and magnesium, showcasing the industry preferences and efficiency based on material properties.
The Die Casting Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Die casting involves a precise process that creates metal parts efficiently. It’s important to understand each step involved in the die casting process. First, molten metal is injected into a reusable mold. This mold is typically made from steel or iron, ensuring durability. Industry reports indicate that die casting can produce parts with complex shapes and high tolerances, usually within 0.1 mm. The ability to maintain such accuracy is one reason die-cast parts are popular in automotive and electronics industries.
Once the metal cools and solidifies, the molds are opened, and the parts are ejected. The entire cycle, from injection to cooling, can take mere seconds to minutes, depending on the part size and material used. However, not every cast is perfect. Some parts may have surface imperfections or trapped air bubbles. Correcting these issues requires a thorough understanding of both mold design and material properties. Reports suggest that eliminating defects benefits production efficiency by up to 30%.
In addition, the reuse of molds in die casting means significant cost savings. A well-maintained die can last thousands of cycles, but wear and tear still occur over time. Regular inspections and adjustments are essential to maintain quality. As manufacturers push for greater efficiency, innovations continue to emerge, albeit not without challenges. Each of these improvements requires careful consideration of the trade-offs involved.
Materials Used in Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds are crucial for producing high-quality metal parts. The materials used in these molds play a significant role in their performance and durability. Most common materials include steel and aluminum. Steel molds are robust and long-lasting. They can withstand high-pressure applications. However, they are more expensive and require more time to manufacture.
Aluminum molds, on the other hand, are lighter and can be produced quickly. They are ideal for low-volume production runs. But, they wear out faster than steel molds. This trade-off is important for manufacturers to consider. They need to balance cost and longevity against production volume.
Tips: Choosing the right material depends on your specific needs. Consider the part complexity and production frequency. Asking for expert advice can help make a better choice. Regularly inspecting molds can prevent unexpected failures. Look out for wear signs early, as this can save costs down the line.
Factors Influencing the Design of Die Casting Molds
Designing die casting molds involves multiple factors. Material choice is crucial. Molds can be made from steel or aluminum. Steel molds last longer but are costlier upfront. Aluminum molds are easier to manufacture. However, they wear out more quickly.
Temperature control is another key aspect. Maintaining the right temperature affects the metal's flow and cooling time. If the mold is too cold, it can lead to defects. If it's too hot, the metal may warp. This balance is often difficult to achieve. Inadequate temperature management can cause production delays.
Surface finish plays a vital role too. A smooth surface helps with metal release. However, achieving this requires precise machining. Many designers overlook the necessity of regular mold maintenance. This negligence can lead to increased costs over time. Each design requires careful consideration of these elements to ensure optimal performance.